Memory is AI's Biggest Bottleneck
Platforms added memory in 2025. So why are you still repeating yourself every session?

Here's the #1 thing holding AI back today:
Not the measured stuff like intelligence or hallucination rates...
It's the fact that you explained your project yesterday.
And today AI's acting like you've never met.
I'm talking memory.
It's a glaring limitation that's hardly mentioned.
You might think AI already has memory.
And you're not wrong.
The memory features rolled out in 2025 are genuinely helpful.
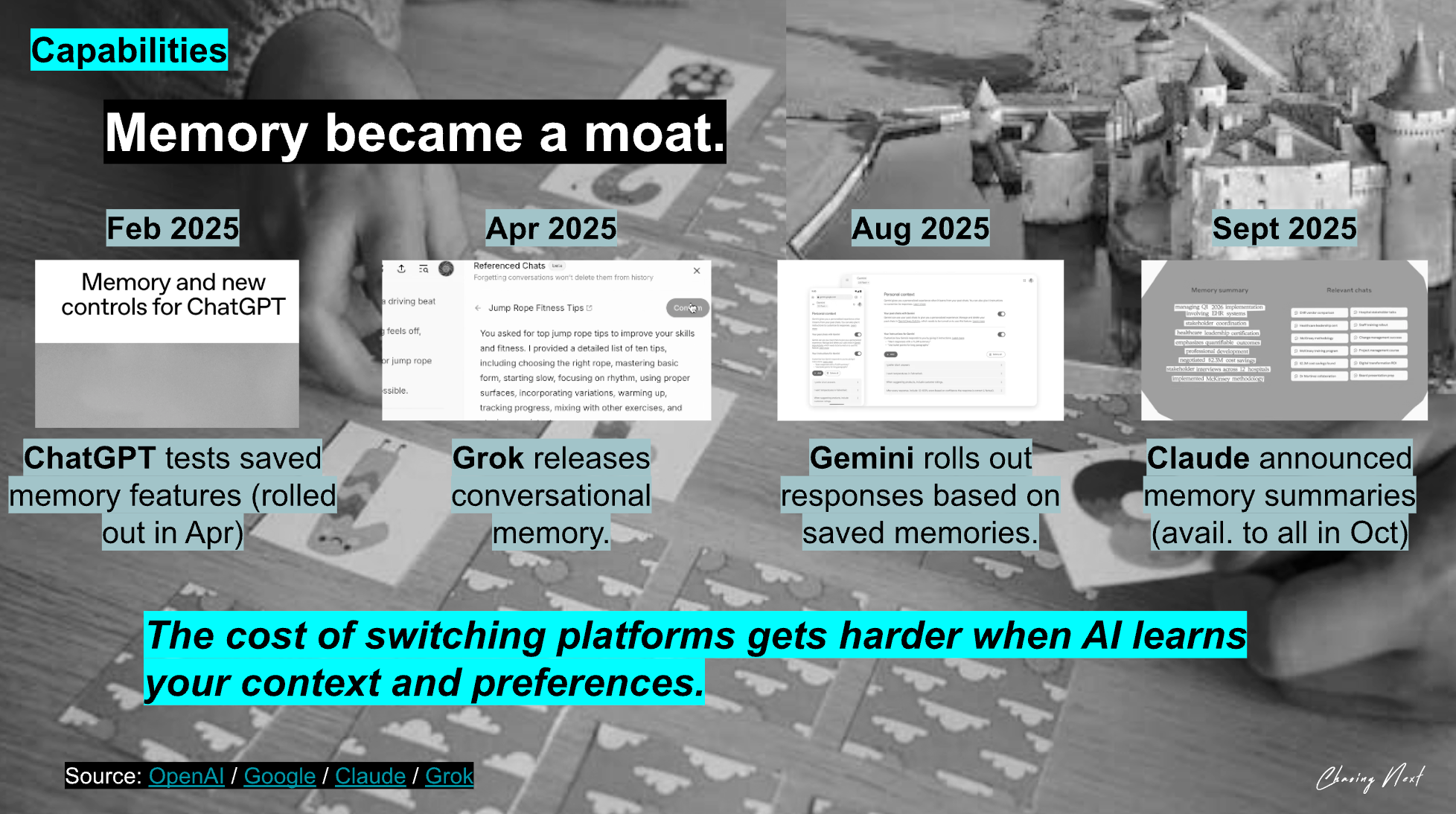
When they work well, they save you from having to restate everything.
But they're not dynamic like human memory.
And their lack of fluidity is stunting AI's ability to take on more.
How today's memory features work:
OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, and Grok all use a similar approach.
Much like RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), though their implementations differ.
The process:
- AI stores summaries about you (brief snippets from past convos).
- When you prompt AI, it searches those notes and finds what seems relevant.
- AI then gives you a response using your input + what it retrieved.
How the top platforms' memory features stack up:
| Platform | How Memory Works | Barriers |
|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Stores memories you explicitly tell it + automatically extracts details from past chats. Prioritizes what stays active based on recency and frequency. | Automatically deprioritizes older memories without telling you. You may want to manually review and clean up if you need precise control. |
| Claude | Maintains persistent memory for your account. Can create memory spaces per project so separate work doesn't bleed together. Recalls past work automatically. | It's not always obvious what it remembered or why. You may need to curate each project's memory over time. |
| Gemini | Stores preferences and context from your chats. Can now connect data across Gmail, Photos, and other Google apps with Personal Intelligence. | Each chat historically feels disconnected. Cross-app features require opt-in and aren't available everywhere yet. |
| Grok | Beta feature that stores preferences and conversation details to personalize responses. | Currently feels less detailed and configurable than the others. You can't easily see or edit what it stored. Still rolling out in beta. |
From my POV, ChatGPT has had the best memory capabilities so far.
But it's still far from behaving like a person would.
Think about talking to a friend or coworker.
They remember what you told them and can build on past convos.
Filtering what's important.
Loosely recalling something random, but relevant, from a year ago.
Overriding and prioritizing as more info comes in.
Today's AI doesn't do this.

It tries, but it's working from small snippets instead of the robust context a person can accumulate over time.
This leaves us building workarounds and micro-managing because we have to.
How top users work around memory gaps:
The people paving the way with AI may not realize they're compensating for memory limitations...
But that's what's happening.
Here's what's working right now:
- Building External Memory Systems
Link: How to Set Up Claude Code in <15 Mins (for Beginners)
- Structuring Setup
Link: 10 Prompting Tactics AI Experts Use
- Defining Rules
Link: How to Set Up Claude Skills in <15 Mins (for Beginners)
I'm not listing these to overwhelm you.
This is just the reality of how you have to build AI workflows right now.
Where memory is heading:
The workarounds we just covered?
Important today, but most of them are temporary.
As memory improves, it will transform from a tool to a coworker.
And ultimately, that's when agentic systems will scale.
To get there, AI platforms and start-ups are working on:
| Focus Area | What This Means |
|---|---|
| Better Structure | Memory gets organized by type (preferences, facts, tasks, decisions) instead of raw clipped text dumps. Makes retrieval smarter and forgetting more intentional. |
| Smarter Architecture | Improved continual learning, nested and long-term memory, and better retrieval planning. The technical foundations necessary for memory to work reliably. |
| More Control | Better UIs to see, edit, and delete memories. When AI uses a memory, it tells you where it came from. |
But as quick as we're moving, we're still a little ways off:
| Timeline | What to Expect |
|---|---|
| 1-2 Years | Memory is still fragmented. Each platform has its own system. You'll see more project-level memory in tools. Better cross-chat memory in assistants. But still different platforms with different approaches. |
| 2-5 Years | More unified. Standards emerge (memory APIs). Different agents will be able to talk to a shared memory layer, one central knowledge hub that all your AI tools plug into, regardless of platform. |
Whoever solves memory will change how we work with AI entirely.
(and FWIW, I think that's when we reach AGI).
For now, you'll get pretty far understanding the limitations and designing around them.